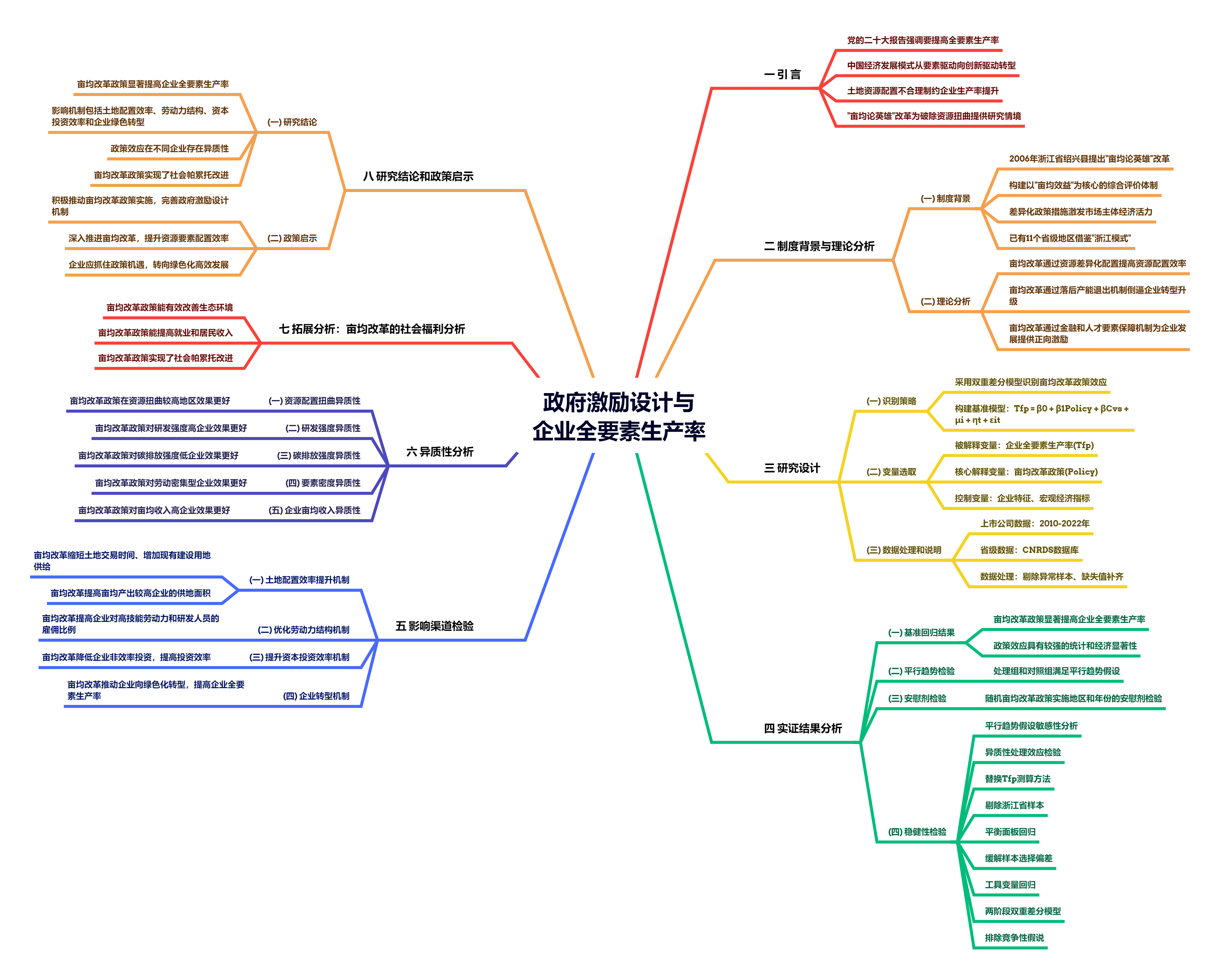
创新性的政府激励设计是中国从要素投入型向全要素生产率推动型增长模式转变的重要制度保障。文章以政府实施的“亩均论英雄”改革政策为契机,从政府的外部激励视角构建了一个分析框架,进而评估了亩均改革政策对企业全要素生产率的影响和机理。研究发现,亩均改革政策的实施使企业全要素生产率提高了2.4%,这一结论在经过一系列稳健性测试后依旧成立。影响渠道检验发现,亩均改革政策对企业全要素生产率的提升作用主要通过提高土地配置效率、优化劳动力结构、提高资本投资效率和推动企业绿色转型来实现。异质性分析发现,亩均改革对企业全要素生产率的提升作用主要体现在研发投入较高、碳排放水平较低、资本密集型、亩均规模较大的企业和资源配置扭曲程度较高地区的企业。进一步研究发现,亩均改革政策不以牺牲居民就业和收入为代价,可以显著减少资源消耗和污染物排放,是实现社会帕累托改进的重要举措。文章从企业生产效率视角揭示了地方政府实施亩均改革政策的微观经济效应,研究结论为深化地方经济治理和完善机制设计以推动企业高质量发展提供了重要政策启示。
政府激励设计与企业全要素生产率——来自“亩均论英雄”改革的证据
摘要
参考文献
相关附件
思维导图
6 贾俊雪,罗理恒,顾嘉. 地方政府环境规制与经济高质量发展[J]. 中国工业经济,2023,(5):99−117.
12 刘守英,王志锋,张维凡,等. “以地谋发展”模式的衰竭——基于门槛回归模型的实证研究[J]. 管理世界,2020,(6):80−92. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-5502.2020.06.007
13 彭远怀. 政府数据开放的价值创造作用:企业全要素生产率视角[J]. 数量经济技术经济研究,2023,(9):50−70.
18 王林辉,姜昊,董直庆. 工业智能化会重塑企业地理格局吗[J]. 中国工业经济,2022,(2):137−155.
19 王永钦,董雯. 机器人的兴起如何影响中国劳动力市场?——来自制造业上市公司的证据[J]. 经济研究,2020,(10):159−175.
20 王正新,龚吉明,严祥武. 资源要素差别化配置的产业升级效应——基于“亩均论英雄”改革的经验研究[J]. 浙江社会科学,2022,(12):26−36. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-2253.2022.12.zjshkx202212003
25 袁堂军. 中国企业全要素生产率水平研究[J]. 经济研究,2009,(6):52−64.
26 张莉,程可为,范子英. 产业用地配置改革与城市内土地错配——基于微观企业土地存量数据的研究[J]. 经济学(季刊),2024,(2):465−480.
27 张莉,程可为,赵敬陶. 土地资源配置和经济发展质量——工业用地成本与全要素生产率[J]. 财贸经济,2019,(10):126−141. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-8102.2019.10.009
28 张少辉,余泳泽. 土地出让、资源错配与全要素生产率[J]. 财经研究,2019,(2):73−85.
29 赵宸宇,王文春,李雪松. 数字化转型如何影响企业全要素生产率[J]. 财贸经济,2021,(7):114−129. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-8102.2021.07.008
30 周黎安. 晋升博弈中政府官员的激励与合作——兼论我国地方保护主义和重复建设问题长期存在的原因[J]. 经济研究,2004,(6):33−40.
31 Aw B Y,Roberts M J,Xu D Y. R&D investment,exporting,and productivity dynamics[J]. American Economic Review,2011,101(4):1312−1344. DOI:10.1257/aer.101.4.1312
32 Biasi B,Sarsons H. Flexible wages,bargaining,and the gender gap[J]. The Quarterly Journal of Economics,2022,137(1):215−266.
33 Callaway B,Sant’Anna P H C. Difference-in-differences with multiple time periods[J]. Journal of Econometrics,2021,225(2):200−230. DOI:10.1016/j.jeconom.2020.12.001
34 De Chaisemartin C,d'Haultfoeuille X. Difference-in-differences estimators of intertemporal treatment effects[J]. Review of Economics and Statistics,2024:1-45.
35 Goodman-Bacon A. Difference-in-differences with variation in treatment timing[J]. Journal of Econometrics,2021,225(2):254−277. DOI:10.1016/j.jeconom.2021.03.014
36 Heim B T,Meyer B D. Work costs and nonconvex preferences in the estimation of labor supply models[J]. Journal of Public Economics,2004,88(11):2323−2338. DOI:10.1016/j.jpubeco.2003.07.009
37 Hsieh C T,Klenow P J. Misallocation and manufacturing TFP in China and India[J]. The Quarterly Journal of Economics,2009,124(4):1403−1448. DOI:10.1162/qjec.2009.124.4.1403
38 Li J,Shan Y,Tian G,et al. Labor cost,government intervention,and corporate innovation:Evidence from China[J]. Journal of Corporate Finance,2020,64:101668. DOI:10.1016/j.jcorpfin.2020.101668
39 Manova K,Yu Z. Multi-product firms and product quality[J]. Journal of International Economics,2017,109:116−137. DOI:10.1016/j.jinteco.2017.08.006
40 Mansfield E. The R&D tax credit and other technology policy issues[J]. American Economic Review,1986,76(2):190−194.
41 Pan W,Xie T,Wang Z,et al. Digital economy:An innovation driver for total factor productivity[J]. Journal of Business Research,2022,139:303−311. DOI:10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.09.061
42 Rambachan A,Roth J. A more credible approach to parallel trends[J]. Review of Economic Studies,2023,90(5):2555−2591. DOI:10.1093/restud/rdad018
43 Restuccia D,Rogerson R. The causes and costs of misallocation[J]. Journal of Economic Perspectives,2017,31(3):151−174. DOI:10.1257/jep.31.3.151
44 Richardson S. Over-investment of free cash flow[J]. Review of Accounting Studies,2006,(11):159−189.
45 Roth J,Sant’Anna P H C,Bilinski A,et al. What’s trending in difference-in-differences? A synthesis of the recent econometrics literature[J]. Journal of Econometrics,2023,235(2):2218−2244. DOI:10.1016/j.jeconom.2023.03.008
46 Wicki S,Hansen E G. Green technology innovation:Anatomy of exploration processes from a learning perspective[J]. Business Strategy and the Environment,2019,28(6):970−988. DOI:10.1002/bse.2295
引用本文
王荣基, 王珏. 政府激励设计与企业全要素生产率——来自“亩均论英雄”改革的证据[J]. 财经研究, 2024, 50(9): 139-153.
导出参考文献,格式为:
上一篇:人工智能、财政支出与制造业升级





 4933
4933  7011
7011