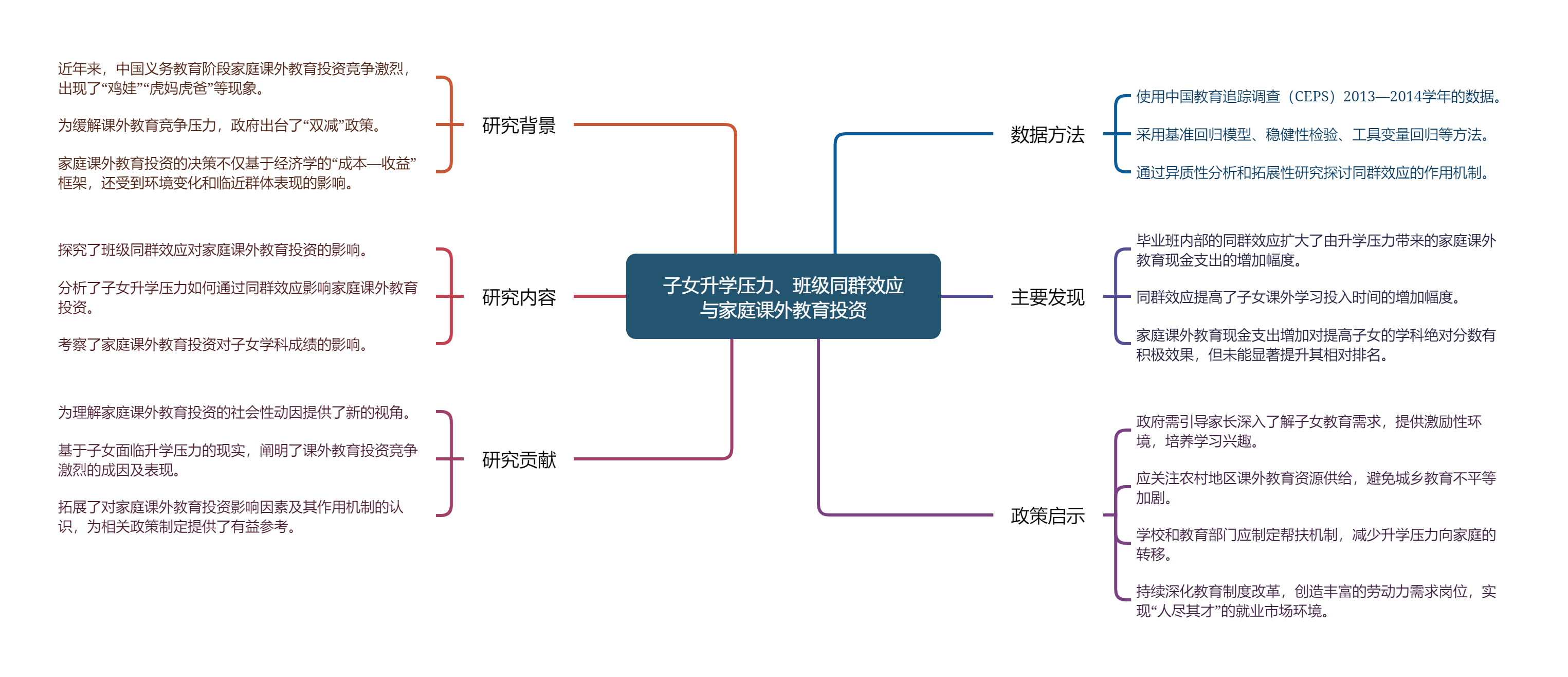
近年来,我国义务教育阶段的家庭课外教育投资竞争激烈问题不断凸显。“双减”政策正是对上述现象的及时纠偏。为了进一步科学有效落实“双减”政策,增强教育获得感,厘清家庭课外教育投资的影响因素及其作用机制必不可少。家庭在课外教育投资中除了遵循经济学传统的“成本—收益”权衡框架外,特定的环境变化以及临近群体的表现对于家庭教育决策也存在重要的影响。基于此,文章运用中国教育追踪调查(
子女升学压力、班级同群效应与家庭课外教育投资
摘要
参考文献
相关附件
思维导图
摘要
9 刘斌,李磊,莫骄. 幸福感是否会传染[J]. 世界经济,2012,(6):132−152.
13 邢春冰,教育扩展、迁移与城乡教育差距——以大学扩招为例[J]. 经济学(季刊),2014,(1): 207−232.
14 薛海平. 从学校教育到影子教育:教育竞争与社会再生产[J]. 北京大学教育评论,2015,(3): 47−69. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-9468.2015.03.004
16 张川川. “中等教育陷阱?”——出口扩张、就业增长与个体教育决策[J]. 经济研究,2015,(12):115−127.
19 Angrist J D,Lang K. Does school integration generate peer effects?Evidence from Boston’s Metco Program[J]. American Economic Review, 2004,94(5):1613−1634. DOI:10.1257/0002828043052169
20 Atkin D. Endogenous skill acquisition and export manufacturing in Mexico[J]. American Economic Review,2016,106(8):2046−2085. DOI:10.1257/aer.20120901
21 Becker G S. Investment in human capital: A theoretical analysis[J]. Journal of Political Economy,1962,70(5,Part 2): 9−49.
22 Carman K G,Zhang L. Classroom peer effects and academic achievement: Evidence from a Chinese middle school[J]. China Economic Review,2012,23(2): 223−237. DOI:10.1016/j.chieco.2011.10.004
23 Chen Y,Fan Z Y, Gu X M, et al. Arrival of young talent: The send-down movement and rural education in China[J]. American Economic Review,2020,110(11): 3393−3430. DOI:10.1257/aer.20191414
24 Duflo E. Schooling and labor market consequences of school construction in Indonesia:Evidence from an unusual policy experiment[J]. American Economic Review,2001,91(4):795−813. DOI:10.1257/aer.91.4.795
25 Duflo E,Dupas P,Kremer M. Peer effects,teacher incentives,and the impact of tracking:Evidence from a randomized evaluation in Kenya[J]. American Economic Review,2011,101(5):1739−1774. DOI:10.1257/aer.101.5.1739
26 Gao Q,Zhai F H,Yang S,et al. Does welfare enable family expenditures on human capital?Evidence from China[J]. World Development,2014,64:219−231. DOI:10.1016/j.worlddev.2014.06.003
27 Glaeser E L,Scheinkman J A,Sacerdote B I. The social multiplier[J]. Journal of the European Economic Association,2003,1(2−3):345−353. DOI:10.1162/154247603322390982
28 Guo J C,Qu X. Competition in household human capital investments:Strength,motivations and consequences[J]. Journal of Development Economics,2022,158: 102937. DOI:10.1016/j.jdeveco.2022.102937
29 Hyman H H. The psychology of status[J]. Archives of Psychology (Columbia University),1942,269:94
30 Kelley H H. Two Functions of Reference Groups[M]. New York:Henry Holt Company,1952,410−414.
31 Knight J,Gunatilaka R. Is happiness infectious?[J]. Scottish Journal of Political Economy,2017,64(1):1−24. DOI:10.1111/sjpe.12105
32 Lavy V,Schlosser A. Mechanisms and impacts of gender peer effects at school[J]. American Economic Journal:Applied Economics,2011,3(2):1−33. DOI:10.1257/app.3.2.1
33 Manski C F. Identification of endogenous social effects:The reflection problem[J]. The Review of Economic Studies, 1993, 60(3):531−542. DOI:10.2307/2298123
34 Manski C F. Economic analysis of social interactions[J]. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 2000,14(3):115−136. DOI:10.1257/jep.14.3.115
35 Nie P,Sousa-Poza A,He X B. Peer effects on childhood and adolescent obesity in China[J]. China Economic Review,2015,35:47−69. DOI:10.1016/j.chieco.2015.06.002
36 Pan Z,Lien D,Wang H. Peer effects and shadow education[J]. Economic Modelling,2022,111:105822. DOI:10.1016/j.econmod.2022.105822
37 Sacerdote B. Peer effects in education:How might they work,how big are they and how much do we know thus far?[A]Hanushek E A,Machin S,Woessmann L. Handbook of the Economics of Education[M]. Amsterdam:Horth-Holland Publishing Company, 2011,3:249−277.
38 Winston G C,Zimmerman D J. Peer effects in higher education. [A]Hoxby C M. College choices:The economics of where to go,when to go,and how to pay for it[M]. Chicago:University of Chicago Press,2004:395−424.
39 Xiao Y,Li L,Zhao L Q. Education on the cheap:The long-run effects of a free compulsory education reform in rural China[J]. Journal of Comparative Economics,2017,45(3):544−562. DOI:10.1016/j.jce.2017.07.003
引用本文
任伟聪, 梁若冰. 子女升学压力、班级同群效应与家庭课外教育投资[J]. 财经研究, 2024, 50(2): 154-168.
导出参考文献,格式为:





 4589
4589  7014
7014