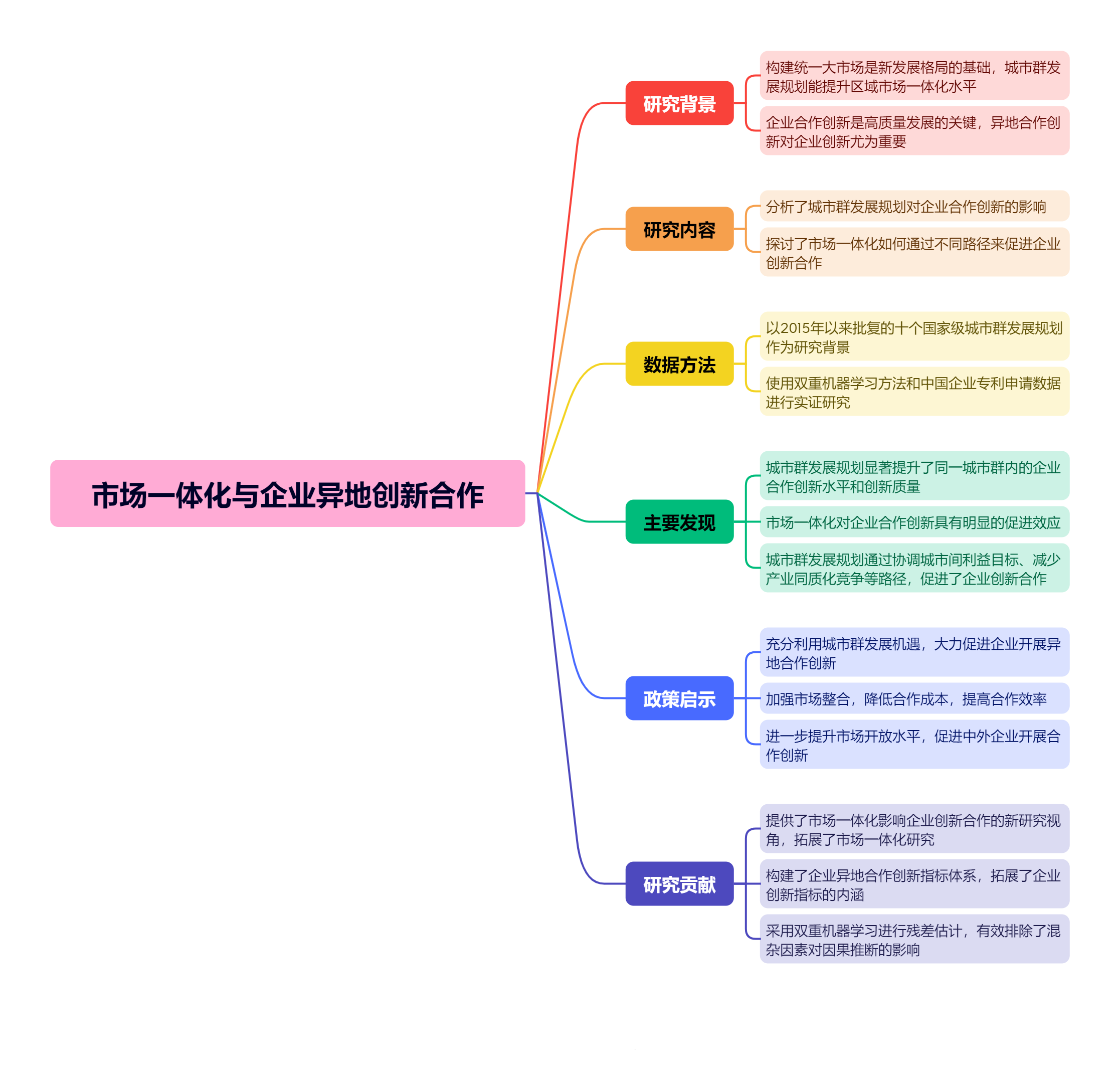
建设统一大市场是构建新发展格局的基础支撑和内在要求。国家层面的城市群发展规划有利于提升区域市场一体化水平和资源配置能力,为企业合作创新奠定了良好的基础。文章以2015年以来国务院先后批复实施的十个国家级城市群发展规划为研究背景,利用双重机器学习方法和中国企业专利申请数据识别城市群发展带来的市场一体化效应对企业合作创新的影响。实证结果显示:城市群发展规划实施后,同一城市群内城市对的企业合作创新水平和创新质量得到了显著提高,市场一体化对企业合作创新具有明显的促进效应。异质性分析显示:由于产权性质和行业特征的不同,市场一体化对企业异地创新合作的影响在国内企业组别中更为明显,外资企业与国内企业的异地合作还有待提升。路径检验表明:国家级城市群规划实施能够通过协调城市间利益目标、减少产业同质化竞争等路径促进企业开展创新合作。机制分析显示:中心城市引导能够进一步强化国家级城市群建设对企业异地合作创新的促进效应。基于实证结果,文章提出了应充分利用城市群发展机遇、大力促进企业开展异地合作创新、加强市场整合、降低企业合作成本等政策建议。
市场一体化与企业异地创新合作*——基于城市群发展规划的实证研究
摘要
参考文献
相关附件
思维导图
2 陈强. 机器学习及R应用[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社,2020.
9 聂辉华. 政企合谋与经济增长:反思“中国模式”[M]. 北京:中国人民大学出版社,2013.
19 Andersson D,Berger T,Prawitz E. Making a market:Infrastructure,integration,and the rise of innovation[J]. The Review of Economics and Statistics,2023,105(2):258−274. DOI:10.1162/rest_a_01067
20 Armstrong C,Kepler J D,Samuels D,et al. Causality redux:The evolution of empirical methods in accounting research and the growth of quasi-experiments[J]. Journal of Accounting and Economics,2022,74(2−3):101521. DOI:10.1016/j.jacceco.2022.101521
21 Audretsch B D,Belitski M. The limits to open innovation and its impact on innovation performance[J]. Technovation,2023,119:102519. DOI:10.1016/j.technovation.2022.102519
22 Balland P A,Boschma R,Frenken K. Proximity and innovation:From statics to dynamics[J]. Regional Studies,2015,49(6):907−920. DOI:10.1080/00343404.2014.883598
23 Bathelt H,Malmberg A,Maskell P. Clusters and knowledge:Local buzz,global pipelines and the process of knowledge creation[J]. Progress in Human Geography,2004,28(1):31−56. DOI:10.1191/0309132504ph469oa
24 Boschma R. Proximity and innovation:a critical assessment[J]. Regional Studies,2005,39(1):61−74. DOI:10.1080/0034340052000320887
25 Boschma R A,Frenken K. The spatial evolution of innovation networks:A proximity perspective[A]. Boschma R A,Martin R. The handbook of evolutionary economic geography[M]. Cheltenham:Edward Elgar Publishing,2010.
26 Brem A,Voigt K I. Integration of market pull and technology push in the corporate front end and innovation management—Insights from the German software industry[J]. Technovation,2009,29(5):351−367. DOI:10.1016/j.technovation.2008.06.003
27 Chen H J,Xie F J. How technological proximity affect collaborative innovation? An empirical study of China’s Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Journal of Management Analytics,2018,5(4):287−308. DOI:10.1080/23270012.2018.1478329
28 Chernozhukov V,Chetverikov D,Demirer M,et al. Double/debiased/neyman machine learning of treatment effects[J]. American Economic Review,2017,107(5):261−265. DOI:10.1257/aer.p20171038
29 Hall B,Helmers C,Rogers M,et al. The choice between formal and informal intellectual property:A review[J]. Journalof Economic Literature,2014,52(2):375−423. DOI:10.1257/jel.52.2.375
30 Hall B H,Sena V. Appropriability mechanisms,innovation,and productivity:Evidence from the UK[J]. Economics of Innovation and New Technology,2017,26(1-2):42−62. DOI:10.1080/10438599.2016.1202513
31 Jaffe A B,Trajtenberg M,Henderson R. Geographic localization of knowledge spillovers as evidenced by patent citations[J]. The Quarterly Journal of Economics,1993,108(3):577−598. DOI:10.2307/2118401
32 Li H B,Zhou L A. Political turnover and economic performance:The incentive role of personnel control in China[J]. Journal of Public Economics,2005,89(9-10):1743−1762. DOI:10.1016/j.jpubeco.2004.06.009
33 Mattes J. Dimensions of proximity and knowledge bases:Innovation between spatial and non-spatial factors[J]. Regional Studies,2012,46(8):1085−1099. DOI:10.1080/00343404.2011.552493
34 McCann B T,Folta T B. Performance differentials within geographic clusters[J]. Journal of Business Venturing,2011,26(1):104−123. DOI:10.1016/j.jbusvent.2009.04.004
35 Moulaert F,Sekia F. Territorial innovation models:A critical survey[J]. Regional Studies,2003,37(3):289−302. DOI:10.1080/0034340032000065442
36 Ponds R,Van Oort F,Frenken K. The geographical and institutional proximity of research collaboration[J]. Papers in Regional Science,2007,86(3):423−443. DOI:10.1111/j.1435-5957.2007.00126.x
37 Presutti M,Boari C,Majocchi A,et al. Distance to customers,absorptive capacity,and innovation in high-tech firms:The dark face of geographical proximity[J]. Journal of Small Business Management,2019,57(2):343−361. DOI:10.1111/jsbm.12323
38 Ren S Y,Hao Y,Wu H T. Government corruption,market segmentation and renewable energy technology innovation:Evidence from China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2021,300:113686. DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113686
39 Sauermann H,Haeussler C. Authorship and contribution disclosures[J]. Science Advances,2017,3(11):e1700404. DOI:10.1126/sciadv.1700404
40 Teodoridis F. Understanding team knowledge production:The interrelated roles of technology and expertise[J]. Manage- ment Science,2018,64(8):3625−3648. DOI:10.1287/mnsc.2017.2789
41 Werker C,Korzinov V,Cunningham S. Formation and output of collaborations:The role of proximity in German nanotechnology[J]. Journal of Evolutionary Economics,2019,29(2):697−719. DOI:10.1007/s00191-019-00605-2
42 Xu C G. The fundamental institutions of China’s reforms and development[J]. Journal of Economic Literature,2011,49(4):1076−1151. DOI:10.1257/jel.49.4.1076
43 Yao L,Li J. Intercity innovation collaboration and the role of high-speed rail connections:Evidence from Chinese Co-patent data[J]. Regional Studies,2022,56(11):1845−1857. DOI:10.1080/00343404.2021.2008340
引用本文
王巍, 姜智鑫. 市场一体化与企业异地创新合作*——基于城市群发展规划的实证研究[J]. 财经研究, 2024, 50(4): 49-63.
导出参考文献,格式为:





 4821
4821  6770
6770